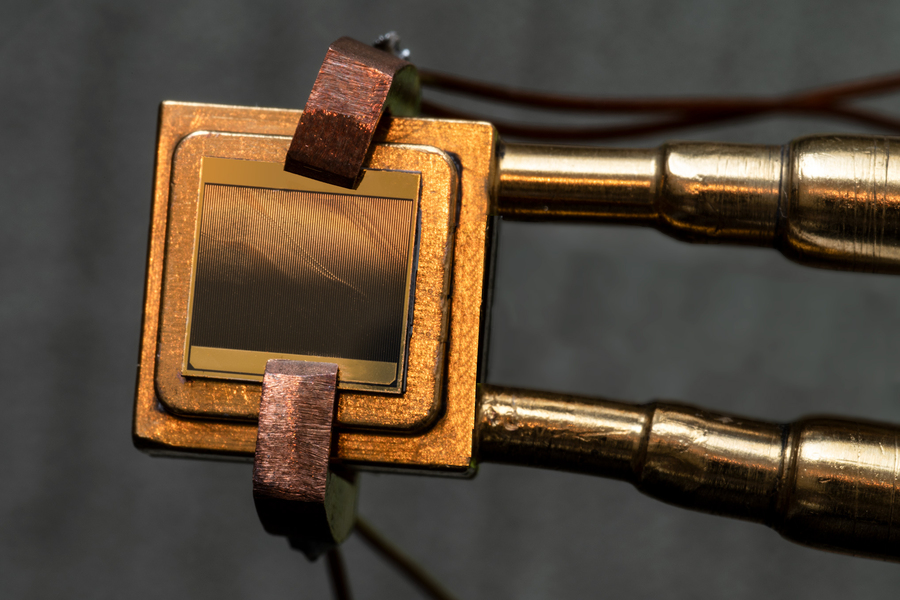
Researchers have revealed a brand new thermophotovoltaic (TPV) mobile that converts warmth to electrical energy with over 40 p.c potency, efficiency nearly on par with conventional steam turbine energy crops. The cells have the prospective for use in grid-scale “thermal batteries,” producing calories dependably and not using a shifting portions.
Thermophotovoltaic cells paintings via heating semiconducting fabrics sufficient to seriously spice up the calories of photons. At excessive sufficient energies, the ones footage can kick an electron around the subject matter’s “bandgap,” producing electrical energy. To this point, TPV cells have accomplished as much as simply 32 p.c potency as a result of they function at decrease temperatures.
In contrast, the brand new design from MIT and the Nationwide Renewable Power Laboratory (NREL) takes energy from white-hot warmth assets between 1,900 to two,400 stage Celsius (3,452 to 4,352 levels F). To do this, it makes use of “high-bandgap” steel alloys sitting over a relatively lower-bandgap alloy.
The high-bandgap layer captures the highest-energy photons from a warmth supply and converts them to electrical energy, whilst lower-energy photons go during the first layer and upload to the voltage. Any photons that run the two-layer gauntlet are mirrored via a reflect again to the warmth supply to save some calories.
That is a completely important step at the trail to proliferate renewable calories and get to an absolutely decarbonized grid.
Measuring the potency the use of a warmth flux sensor, the workforce discovered that energy various with temperature. Between 1,900 to two,400 levels Celsius, the brand new TPV design produced electrical energy with about 40 p.c potency.
Steam generators can ship the similar potency, however are way more difficult and limited to decrease temperatures. “Some of the benefits of solid-state calories converters are that they may be able to function at upper temperatures with decrease upkeep prices as a result of they have got no shifting portions,” MIT Professor Asegun Henry advised MIT Information. “They simply take a seat there and reliably generate electrical energy.”
In a grid-scale thermal battery, the device would take in extra calories from renewable assets just like the solar and retailer it in closely insulated banks of sizzling graphite. When wanted, the TPV cells may then convert that warmth to electrical energy and ship it to the facility grid. The experimental mobile was once only a sq. centimeter, so the workforce must ramp that as much as round 10,000 sq. toes for grid-level energy, however the generation already exists to create cells on that scale, Henry notes.
“Thermophotovoltaic cells had been the closing key step towards demonstrating that thermal batteries are a viable idea,” he mentioned. “That is a completely important step at the trail to proliferate renewable calories and get to an absolutely decarbonized grid.”
All merchandise advisable via Engadget are decided on via our editorial workforce, impartial of our mother or father corporate. A few of our tales come with associate hyperlinks. If you purchase one thing via this sort of hyperlinks, we would possibly earn an associate fee.