Smartphone cameras have gotten relatively excellent, but it surely’s getting tougher and tougher to toughen them as a result of we’ve just about reached the restrict of what’s imaginable within the area of a cubic centimeter. Glass is a startup taking a look to essentially exchange how the digicam works, the use of a far larger sensor and an optical trick from the depths of filmmaking: anamorphic lenses.
It will not be glaring that cameras gained’t recover, since we’ve observed such advances in fresh generations of telephones. However we’ve used up the entire slack left on this line, because it have been.
To toughen the picture, you want a larger sensor, higher lens or some roughly computational wizardry. Sadly, sensors can’t get a lot larger as a result of they’d want larger lenses to check. And lenses can’t get larger as a result of there’s simply no room for them within the telephone frame, even while you “fold” the digicam. In the meantime, computational pictures is excellent, however there’s simplest such a lot it could possibly do — stacking a couple of photographs to recover dynamic vary or intensity data is excellent, however you achieve some extent of diminishing returns beautiful temporarily.
“The restrictions was about value, however now it’s length,” defined Glass co-founder and CEO Ziv Attar, who has labored in cell imaging for over a decade, together with at Apple. The opposite co-founder, Tom Bishop, additionally labored at Apple, the 2 of them running on growing Portrait Mode and most likely chafing on the barriers of conventional digicam design.
“As much as 5 years in the past they simply made the lens wider, then they began making the sensor larger,” Attar mentioned. “Then you definately throw algorithms at it to scale back noise, however even this is achieving its limits; beautiful quickly it’s going to be natural hallucination [i.e. AI-generated imagery]. Evening mode takes publicity stacking to extremes — it offers very effectively with the loss of photons, however in the event you zoom in it begins to seem very bizarre and pretend.”
“The telephone display roughly deceives us,” he persevered. “If you happen to let an ordinary particular person examine an iPhone 12 and 13, they gained’t see the adaptation — however in comparison to a professional digicam, someone can inform. And if you’ll see the adaptation, there’s numerous paintings to do.”
So what’s that paintings, precisely? Attar has made up our minds that of those quite a lot of conundrums, the one person who is sensible to modify is the lens. True, it could possibly’t get any larger — however provided that you’re the use of a standard, symmetrical lens meeting. However why will have to we? They gave up on that constraint a century in the past in cinema.
Anamorphic evolution
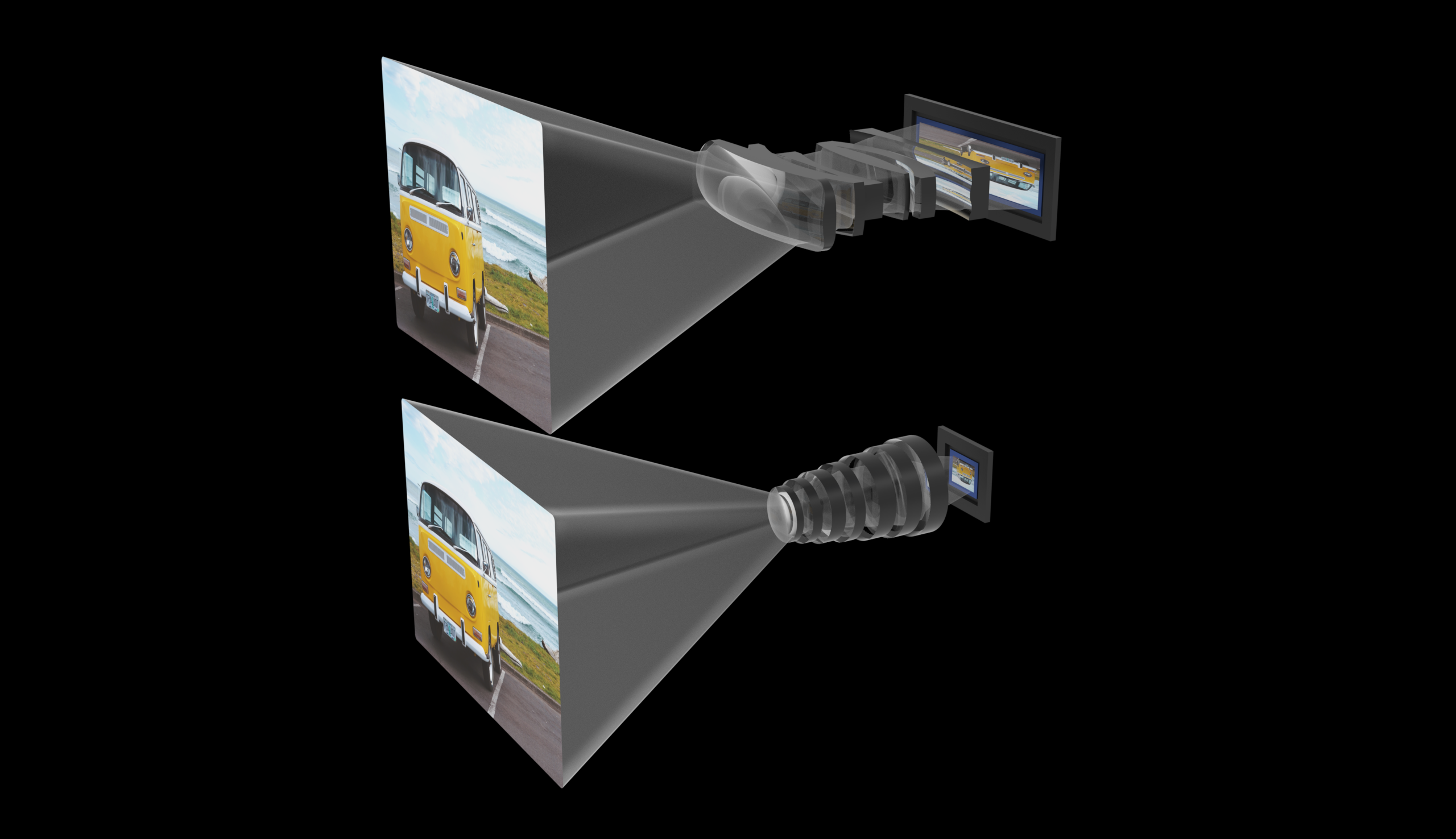

A CG symbol appearing examples of anamorphic (most sensible) and conventional symmetric lenses and the ensuing inner symbol length. Symbol Credit: Glass
Movies weren’t all the time widescreen. At the beginning they have been much more likely to be roughly the form of a 35mm movie body, for glaring causes. If you happen to raveled out the highest and backside, it’s worthwhile to venture a widescreen symbol, which individuals favored — however you have been principally simply zooming in on part of the movie, which you paid for intimately. However a method first examined within the ’20s quickly solved the issue.
Anamorphic lenses squeeze a large box of view from the perimeters so it suits within the movie body, and when projected the use of an anamorphic projector, the method was once reversed — the picture is stretched again out to the specified facet ratio. There are a couple of attention-grabbing optical results offered however… if I describe them you’ll by no means have the ability to un-see them in content material, so I’ll forbear.
The lens machine proposed by means of Glass isn’t relatively the similar, but it surely makes use of an identical ideas and strangely formed lenses. It began from the basic thought of the way to upload a bigger sensor. Merely making a bigger sq. would necessitate a bigger lens, which we will’t do — however what in the event you made the sensor longer, as in a rectangle? Smartly, you’d want a longer, oblong lens too. The anamorphic method manner you’ll seize and venture a bigger however distorted symbol, then convert it to the suitable facet ratio within the symbol processor. (The method isn’t precisely analogous to the movie method but it surely makes use of the similar ideas.)
How a lot better a picture can you seize? Smartly, an iPhone 13’s primary digicam has a sensor about 7×5 millimeters, so 35 sq. mm overall. Glass’s prototype makes use of a sensor that’s about 24×8 mm: about 192 sq. mm, 5-6 occasions better, with a commensurate build up to megapixels. Right here’s slightly chart for informal reference:
Taking into account the fanfare that most often accompanies expanding a telephone’s sensor length by means of 15 or 20 p.c, that’s a huge jump.
However Attar defined that the best way they measure it, it’s much more. If you happen to have been to amplify the picture to the proper facet ratio, it might in reality be two times as tall: 24x16mm, simply shy of the APS-C usual in DSLRs however neatly above the Micro 4 Thirds and 1″ sensors additionally commonplace (and extremely performant) in mirrorless cameras. That results in the corporate’s declare of getting 11 occasions the “imaging house” of an iPhone. The analysis of those metrics is a non-trivial procedure I’m now not provided to do, however in truth both one could be a game-changing improve for a telephone.
Larger, brighter and somewhat more unusual
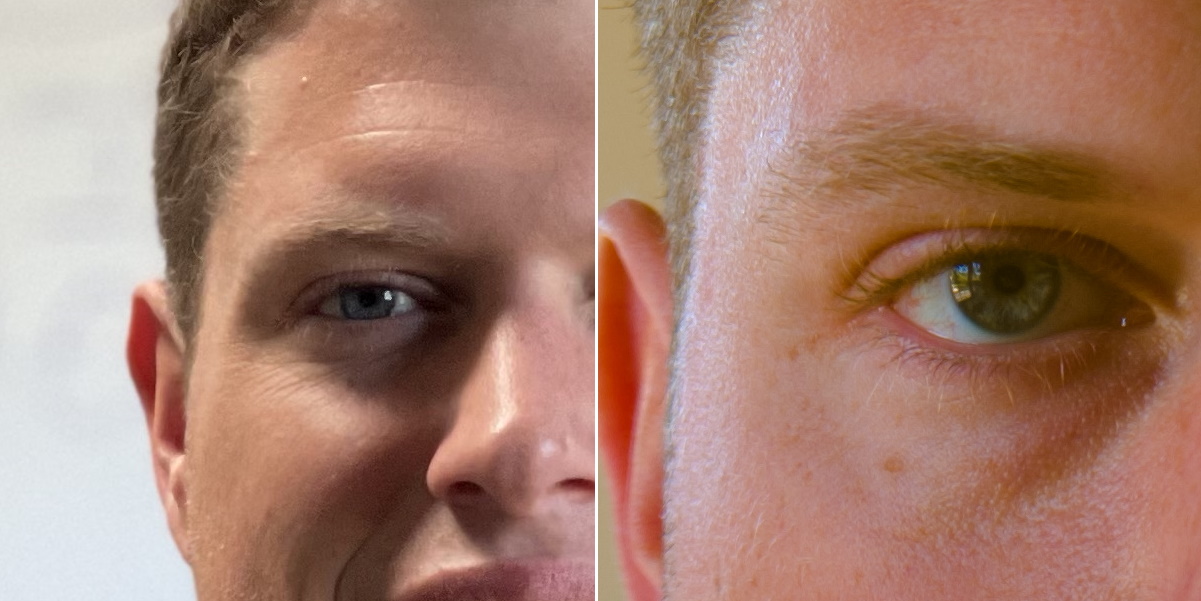
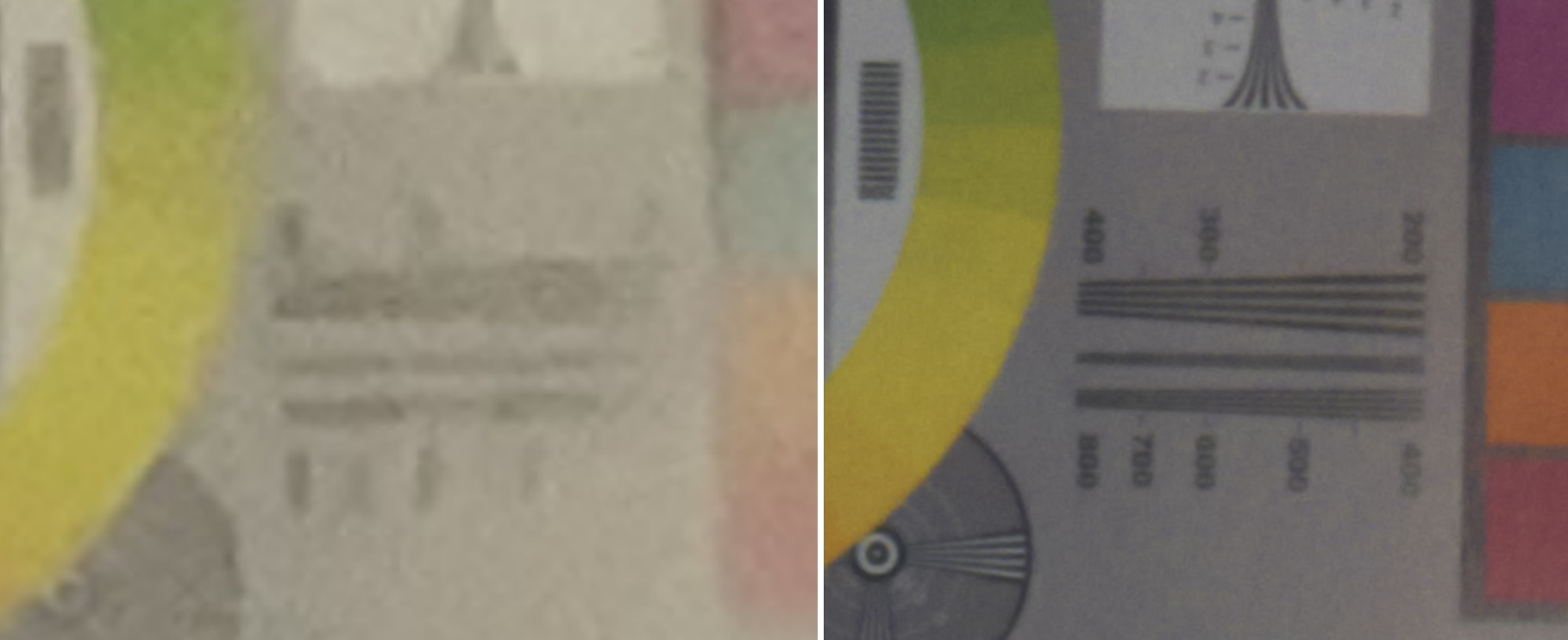
There are advantages and disadvantages to this procedure. Crucial one is an immense build up in gentle collecting and resolving energy. Extra gentle manner higher exposures on the whole and higher photographs in difficult prerequisites — no use for a complicated system studying powered multi-exposure evening mode if you’ll simply… see issues. And there’s a ways, way more element in photographs in comparison with the ones from unusual smartphones.
Observe that the restricted instance above is simply that — it’s onerous to do apples-to-apples comparisons when the focal lengths, symbol processing and output decision are so other (to not point out my cropping and re-encoding), however on the very least you’ll see that an excessive amount of element is added even on this non-optimal presentation. The overall-size authentic photographs are to be had right here: iPhone, Glass.
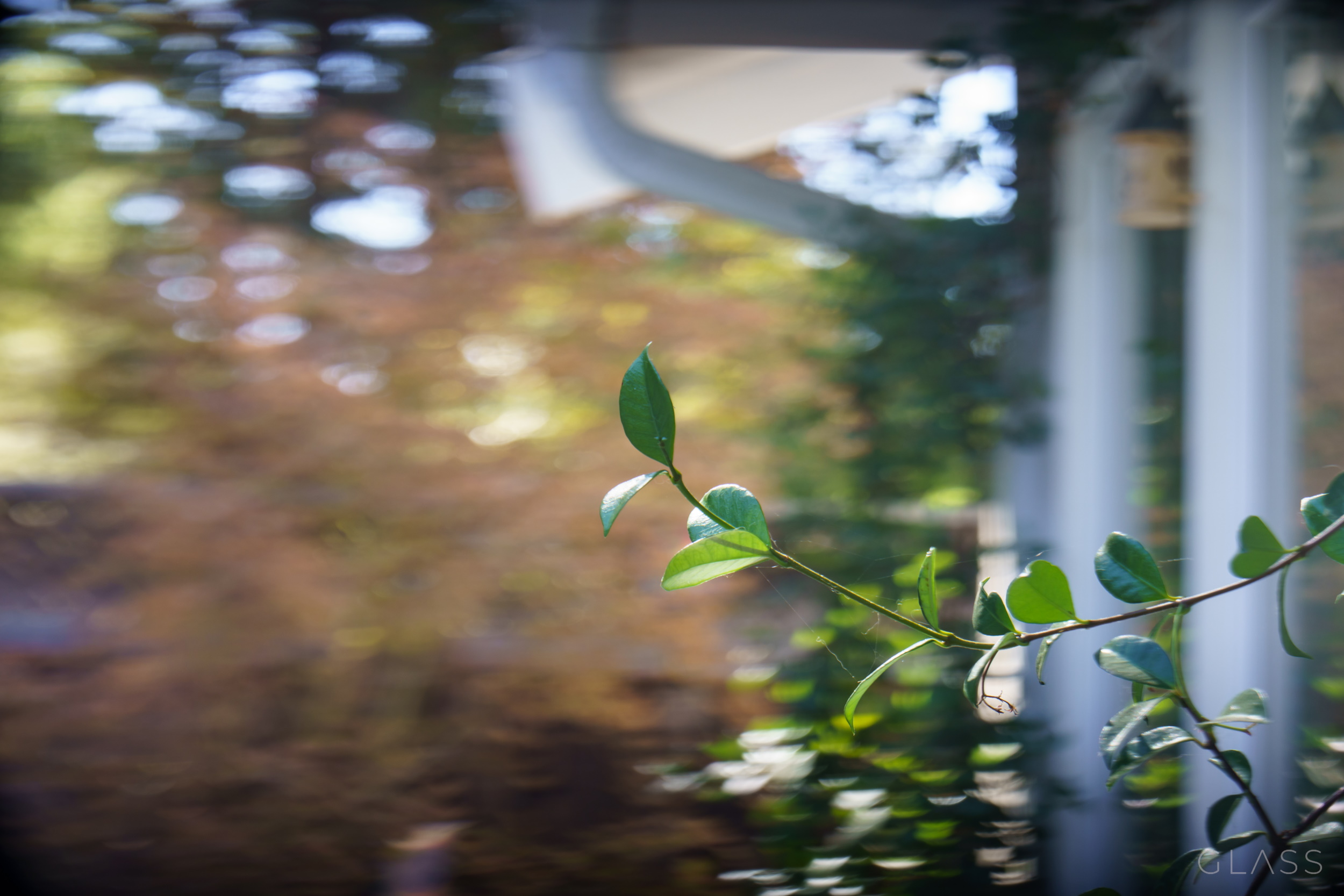
As a result of the bigger sensor and the character of the glass, you additionally get herbal bokeh, or background blur. Portrait mode is in fact a favourite amongst smartphone customers, however even the most productive strategies of simulating bokeh are a ways from absolute best. The similar impact Apple painstakingly simulated lenses to reach happens naturally at the Glass prototype, simply as it might on a bigger virtual digicam. And there’s no probability of the type of bizarre mistake you notice within the AI-segmented photographs, which continuously clip out hair and different main points, or fail to reach the intensity impact in subtler techniques.
Instance symbol appearing portrait mode on an iPhone (left) and the unprocessed Glass shot, which lacks the smoothing and artifacts of the manipulated one. Symbol Credit: Glass
Whilst there could be no optical zoom, Attar identified that zooming in by means of cropping (i.e. virtual zoom) on a Glass machine would assist you to zoom in additional than maximum optical zooms available in the market, and also you’d nonetheless have extra gentle and pixels than the contest. I’m now not usually one to let “virtual zoom is ok” claims reside, however on this case the sheer length of the lens and sensor greater than make up for it.
Those advantages, despite the fact that in brief mentioned, are greater than substantial. The development to gentle and element places it manner out in entrance of the most productive cameras available in the market. (And whilst the smallest main points might break out your realize on a small display, a foul publicity is noticeable at any length.)
Drawbacks are principally to do with the complexities of running a digicam that’s utterly optically other from a conventional one. The mechanisms for autofocus are other (anamorphic center of attention is notoriously complicated) and there are many distortions and aberrations that wish to be corrected for — symmetrical lenses at this length even have distortion and degradation, however of a special kind.
“[Distortions] are all constrained all through design such that we all know prematurely that we will proper for them,” mentioned Attar. “It’s an iterative procedure however we did kick get started construction of a customized devoted tool software to co-optimize lens parameters and neural community variables.” In different phrases they didn’t design anything else they couldn’t proper for.
One impact I in finding disorientating however possibly others will make a decision is trivial is the form of the bokeh. Generally out of center of attention highlights blur out into little translucent discs, however within the Glass machine they get to the bottom of right into a gradient of ovals and obese crescents.
To my neurotic eye that simply isn’t proper. It’s… unnatural. However I can even’t now not realize vignetted bokeh because of french flags in movie and TV (don’t glance it it up — this too is all over and you’ll’t unsee it). And anyway motion pictures shot in anamorphic display an identical bokeh distortion, so it’s in reality relatively commonplace, simply now not in nonetheless photographs and smartphone photographs.
I thought there could be drawbacks because of the wish to stretch the picture digitally — that kind of factor if executed poorly may end up in moiré and different undesirable artifacts. However Attar mentioned it’s remarkably easy to coach a fashion to do it in order that nobody can inform the adaptation aside from pixel peepers: “We educated networks to use 1-D super-resolution according to data from the opposite axes. Once we practice our set of rules it appears to be like love it got here from a complete APS-C sensor, in box of view and determination.”
That can all need to be verified by means of reviewers and digicam professionals when there’s a manufacturing model, however the idea turns out sound and the early effects are greater than promising.
Presently the corporate has moved on from standalone prototypes to a third-generation telephone issue instrument that presentations how the tech will have compatibility into just about any chassis available on the market. There’s not anything unique about it rather then the optical qualities, Attar mentioned, so despite the fact that it gained’t be as reasonable to fabricate as as of late’s off-the-shelf digicam and symbol processing gadgets, it may be made simply as simply. As he famous, value is infrequently an choice any longer, and if one corporate could make an enormous jump in digicam high quality they are able to seize a big chew of the marketplace.
“We need to persuade a telephone maker to principally ditch the outdated era,” mentioned Attar. “We’re seeing great comments. The one problem is doing it in an affordable time. I’m now not announcing there’s no possibility. However numerous us had excellent jobs at giant firms — we didn’t depart our fancy salaries at Apple to paintings on some BS factor. We had a plan from the start.”
Even supposing an settlement was once struck now with a large cell producer, it might take a yr and part or two years to get to marketplace. “However we need to get started someplace,” he concluded.
Glass has raised $2.2 million in seed investment, led by means of LDV Capital and a selection of angel buyers. In fact that’s now not intended to hide the price of production, however now that the corporate is leaving the lab it’s going to want running money to commercialize even will have to a big producer make a dedication. Greg Gilley, previously Apple’s VP of cameras and pictures, and MIT Media lab’s Ramesh Raskar joined as advisors, rounding out a workforce buyers are prone to have numerous self assurance in.
If the Glass means catches on, be expecting to listen to about different firms claiming to have invented it in rather less than two years.






