The tech business has been hit in particular difficult by means of the pandemic and the Great Resignation, leaving organizations dealing with a dearth of certified process applicants for greater than 1 million openings.
For all US jobs, the collection of openings was once at a top of eleven.5 million on the finish of March, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). In the meantime, in every of the previous six months, greater than 4 million other folks have surrender their jobs, in step with the company.
For era, the ability scarcity is even worse. Whilst the nationwide unemployment price hovers round 3.6%, for the tech business it’s 2%, in step with CompTIA, a non-profit affiliation for the IT business and group of workers. That is brought about employers all the way through the USA to step up their seek for employees — and to revisit the {qualifications} (reminiscent of a four-year school level) they require.
Amongst middle-skilled occupations, the openings that require school levels are, for probably the most section, very similar to the ones openings for which no level is needed, in step with a recent study by means of Harvard Trade College’s (HBS) Challenge on Managing the Long term of Paintings and the Burning Glass Institute.
“Jobs don’t require four-year school levels. Employers do,” the learn about mentioned.
That realization is prompting firms to imagine a shift in hiring practices that acknowledges the non-traditional paths many have taken to expand era qualifications — paths that don’t require a point.
Companies, executive nix level requirement
In June 2020 and January 2021, the White House announced limits on the use of educational requirements when hiring IT pros in choose of a skills-based method.
Closing month, employment web page Indeed printed the result of a survey of 502 employers throughout the USA on how the pandemic has formed present recruiting and long run plans. The consequences: the vast majority of corporations surveyed are moving toward a more flexible model of candidate recruiting.
“Long past are the times of pointless credentials and aspirational process necessities. As an alternative, we discover employers pondering creatively to imagine various kinds of candidates than previously — a shift that may get advantages everybody,” Certainly mentioned within the record.
Particularly, the Certainly survey discovered:
- 59% of employers are taking into account getting rid of school level necessities for hiring.
- 30% of employers imagine disposing of level necessities would lend a hand them rent extra various ability.
- 87% of senior executives say they aren’t ready to handle qualifications gaps.
Most effective about one-third of the USA grownup inhabitants has a faculty level, which makes it more difficult for companies to rent ability, in step with analysis company IDC. That is exacerbated by means of the truth many firms started difficult four-year levels after the Nice Recession of 2008-09, when process applicants have been considerable, IDC mentioned in a 2018 record.
The ones requirements have been anticipated to be lifted because the economic system progressed. However even because the exertions marketplace has tightened, the inflation in school level necessities has remained.
Until an organization units up an inside building program on certifications as occupation milestones, it’s tricky to spot which of them help in making a candidate “another way certified,” in step with Cushing Anderson, an IDC vice chairman in HR analysis.
There’s little chance in bypassing level necessities in choose of skills-based applicants, however company hiring groups are rewarded for being “chance averse,” or presenting handiest the most efficient certified applicants on paper to the hiring supervisor, in step with Anderson.
“The issue is maximum process postings lately nonetheless include an extended record of necessities, which is able to flip away possible process seekers, particularly the ones from nontraditional backgrounds,” Jamie Kohn, a analysis director in Gartner’s Human Useful resource follow mentioned by way of e-mail. “Taking a look forward, probably the most a success firms aren’t simply decreasing necessities — they’re development relationships with change coaching methods to sign their hobby to applicants early on.”
Some employers are already resetting necessities in a number of roles, losing “four-year level” from many middle-skill or even some higher-skill postings, in step with a study by Harvard Business School (HBS) and Burning Glass Institute previous this yr. And whilst the COVID-19 pandemic speeded up the method, that reset started sooner than the disaster — and is prone to proceed.
Talents-based hiring opens the doorways to alternatives
Research have discovered when employers drop level necessities in process postings, they turn out to be extra particular about qualifications, spelling out the cushy qualifications that can had been assumed to come back with a faculty schooling, reminiscent of writing, verbal exchange, and being element orientated.
Tech firns have publicly introduced their dedication to prioritize qualifications over levels in IT occupations. A number of, maximum particularly Accenture, Apple, Google, IBM, and Tesla, have made subject matter adjustments in process necessities throughout their organizations, in accordance HBS and CompTIA. Others have made handiest modest adjustments in necessities for particular positions, suggesting that company commitments haven’t begun to translate to sensible implementation.
“Apple, IBM, Google and Tesla, simply to call a couple of, introduced the removing of the four-year bachelor’s level as an software requirement,” CompTIA mentioned in its record.
Lately, half of of IBM’s US process openings don’t require a four-year level, a convention the corporate began lengthy sooner than the pandemic hit.
 IBM
IBMKelli Jordan, director of Occupation, Talents, and Efficiency for IBM.
“Whilst you take into accounts requiring a bachelor’s level for a task, you’re mechanically shutting out large portions of the inhabitants,” mentioned Kelli Jordan, director of Occupation, Talents, and Efficiency for IBM. “It additionally is helping to make it a extra various business. In the event you’re taking a look on the Black inhabitants, you’re ruling out 72% of that inhabitants and 79% of the Hispanic inhabitants.
“It’s extra about how we’re recalibrating our mindset to take into accounts {qualifications} in a different way,” she mentioned.
IBM continues running to scale back the collection of process openings that require school levels, Jordan mentioned. Task applicants with cushy qualifications are way more fascinating than the ones with technical acumen.
“Technical qualifications, or domain-specific qualifications, are converting so briefly. The half-life of them, or how lengthy they’re in reality legitimate, is shrinking each and every unmarried yr,” she mentioned. “It’s the ones cushy qualifications which can be evergreen. Each and every position goes to want any individual with communications qualifications, with teamwork qualifications, with adaptability. The ones core qualifications are what’s going to lend a hand other folks proceed with the intention to re-skill and up-skill through the years.”
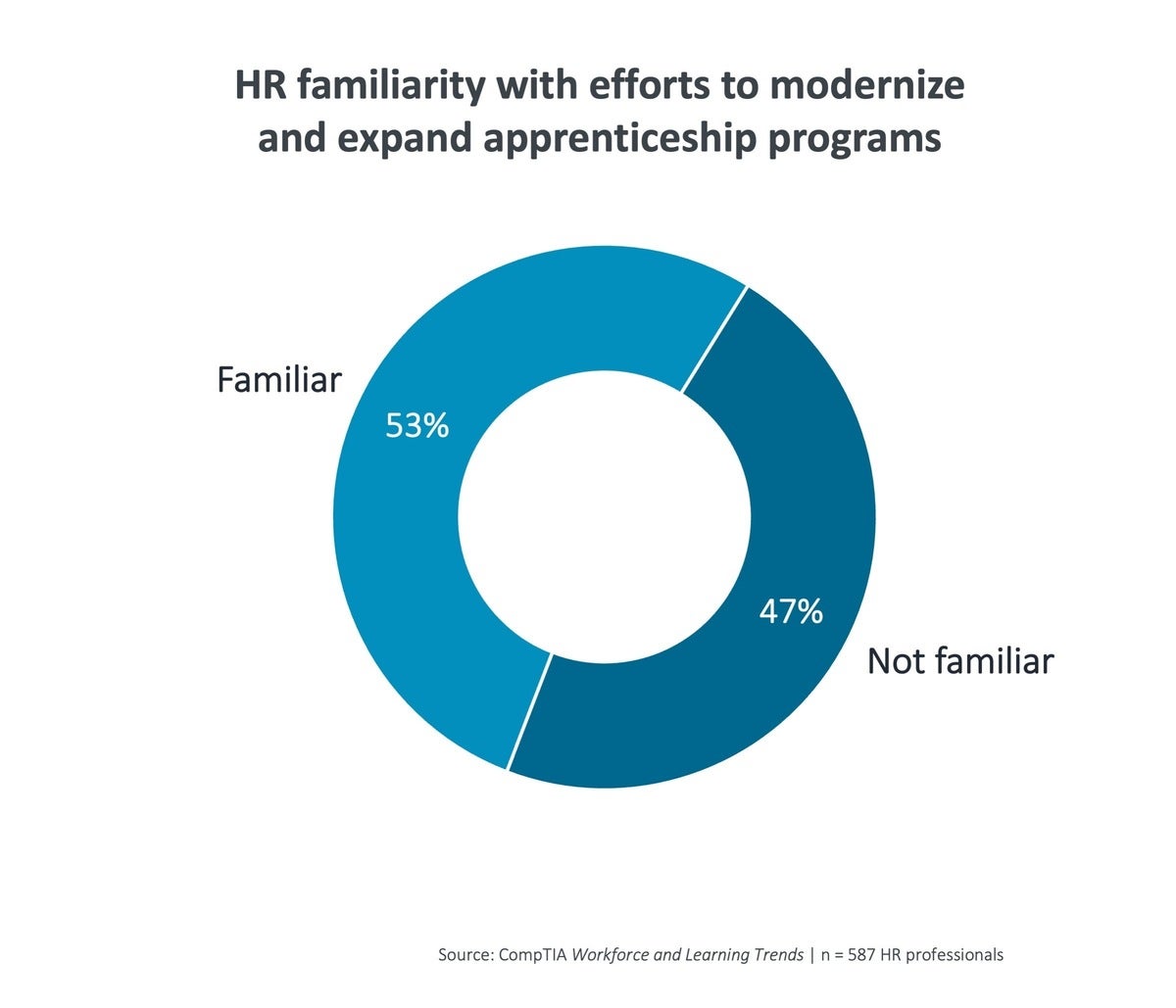 CompTIA
CompTIAJulie Candy, CEO {of professional} services and products large Accenture, advised Harvard Trade Evaluation (HBR) her corporate started revamping its process necessities about 18 months in the past in North The united states with recognize to applicant qualifications; it then expanded that fluctuate globally.
In North The united states, for instance, just about 50% of Accenture’s process openings don’t require four-year levels. (They used to all require four-year levels, Candy mentioned.)
“That right away opens you as much as a broader pool of people who you’ll be able to rent from,” Candy mentioned. “And in reality, about 20% of the folk we if truth be told rent for the ones openings shouldn’t have four-year levels. So, we’ve expanded the pool of people that we will cross after to fill those jobs.”
Accenture added 200,000 other folks to its group of workers right through the previous 18 months from a pool of four.6 million resumes, in step with Candy.
“Some of the vital issues that we search for if truth be told, regardless of who you’re, is your skill to be told — finding out agility,” Candy mentioned. “We ask an easy query to all of our candidates, senior and junior. ‘What have you ever realized within the closing six months that was once now not a part of faculty?’”
Drawing water from your individual smartly
upskilling or reskilling current staff is some other trail firms can take to near the hiring hole.
“Taking a look forward, probably the most a success firms aren’t simply decreasing necessities – they’re development relationships with change coaching methods to sign their hobby to applicants early on,” Gartner’s Kohn mentioned.
That is vital as a result of 58% of process applicants lately say they’ve taken lessons within the closing yr to be told qualifications out of doors in their present process, in step with Gartner.
In adition, the abilities organizations want are converting. In step with Gartner, a 3rd of the abilities required in 2019 is probably not wanted by means of 2024 — and 21% have already misplaced salience.
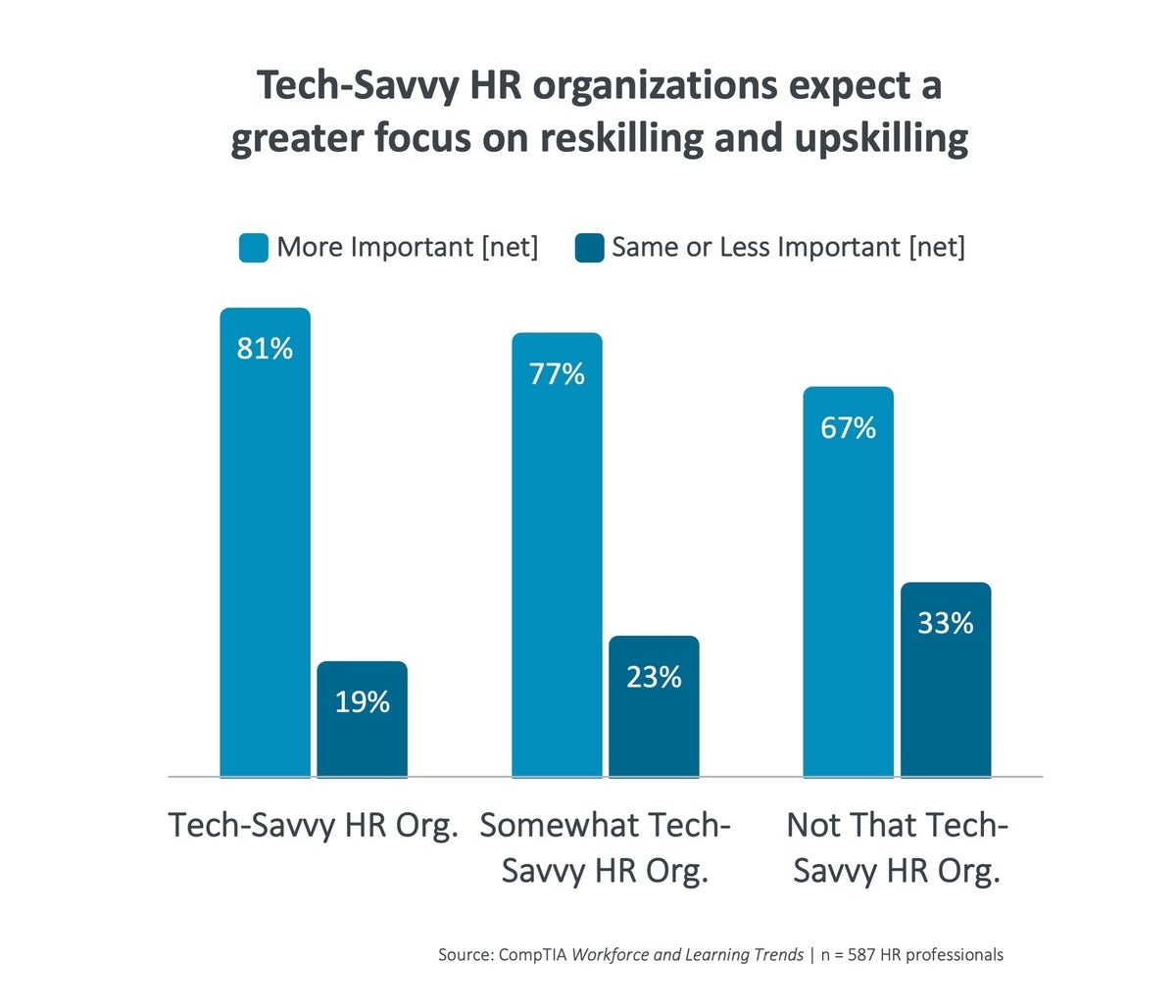 CompTIA
CompTIA“Because of this, we’ve observed an building up in reskilling methods for in particular hard-to-fill tech positions, reminiscent of endeavor structure and knowledge science,” Kohn mentioned. “The hot button is to spot which baseline qualifications give the most efficient likelihood of good fortune for creating the wanted qualifications.”
As an example, along with elementary IT qualifications, some firms focal point on robust trade data and problem-solving skills as qualifiers for a reskilling program.
Talents building is a number one focal point in shaping new occupation pathways at Accenture, in step with Pallavi Verma, a senior managing director. The corporate spends just about $1 billion once a year in finding out {and professional} building for its personal staff.
“We spend money on steady finding out and building, so our other folks stay extremely related, and we praise our other folks to acknowledge their qualifications, contributions, and occupation development,” Verma mentioned. “We’re skilling at scale. There are 8,000-plus qualifications in our library that our other folks can earn, according to their paintings revel in and thru certifications and finding out alternatives.”
At IBM, the typical worker engages in 88 hours of occupation building coaching once a year. Any IBM worker can join structured finding out or mentorship methods, which pair them with extra senior staff who can information them in occupation building.
“We rolled it out now not lengthy after the pandemic began,” mentioned IBM’s Jordan. “It created a digital water cooler. Other folks not had the chance to fulfill any individual within the place of business, however they might meet them just about anyplace on the earth and attach to be told a few explicit capability to lend a hand their occupation trail.”
Firms have additionally greater stipends to pay for worker education schemes. For 2021, 23% of stipends paid by means of organizations have been indexed as Skilled Building, in step with CompTIA. Within the first quarter of 2022, that quantity had virtually doubled to 44%.
In step with CompTIA, {most professional} building compensation claims are for:
- Books associated with their position and tasks;
- Coaching Subscriptions;
- Trade Classes;
- Management lessons and books;
- Coding & programming books and assets;
- And club subscriptions associated with position and tasks.
Firms also are increasing methods to provide extra staff a base-level figuring out of era. The theory is, if we all know a little bit about IT, you wish to have fewer mavens to get the paintings carried out, Kohn mentioned.
Within the first six months of the pandemic, Accenture up-skilled about 100,000 other folks with methods that lasted from 8 to fifteen weeks, relying at the qualifications taught, in accordance Candy.
“And we have been ready to take action very unexpectedly, which enabled us to emerge from the pandemic a lot quicker as a result of lets shift our other folks in opposition to the brand new puts of call for,” Candy mentioned. “And, in fact, it’s a part of what makes Accenture such a stupendous position to paintings, as a result of other folks really feel like they’re repeatedly being invested in.”
A {qualifications} reset may just spice up range
A reset on which exact qualifications are had to fill knowledge-worker jobs can have main implications for a way employers to find ability within the years forward, and open alternatives for the two-thirds of American citizens and not using a school schooling, in step with the HBR/Burning Glass learn about.
“In accordance with those developments, we undertaking that an extra 1.4 million jobs may just open to employees with out school levels over the following 5 years,” the record mentioned.
On the upward push now: the significance of certification methods, a pattern that is obvious in CompTIA’s contemporary survey of HR leaders. Web beef up for getting rid of or stress-free level necessities in hiring greater from 76% to 85% this yr; 76% say certifications are actually a think about IT hiring; and 47% be expecting certifications to turn out to be much more vital as a candidate analysis instrument.
“I’ve two levels, and I will be able to inform you the whole lot I realized in each levels — even sooner than I graduated — was once out of date. Tech leaders have created their very own ability scarcity by means of refusing to rent expert, various pros who possess certification coaching,” mentioned Ida Byrd-Hill, CEO and founding father of Automation Workz.
 Automation Workz
Automation WorkzIda Byrd-Hill, CEO and founding father of Automation Workz
Automation Workz gives reskilling or upskilling methods in tech and cybersecurity to firms and people. The corporate additionally gives govt training and a diversity culture audit to resolve an organization’s inclusivity and easy methods to building up it.
Byrd-Hill, who’s Black, based Automation Workz in 2019 to provide post-secondary tech certifications to provide African-American citizens a clearer trail into the tech business. Born and raised in Flint, MI., Byrd-Hill graduated from the College of Michigan with a point in economics and later were given an MBA. She spent maximum of her occupation running in human assets and fiscal services and products, but additionally did coding in Cobol. One factor that stricken her: she didn’t see different individuals who seemed like her in era.


